Bathroom Safety – Orthodynamic Daily
Enhance your safety with the Orthodynamic Limited Daily Living Mobility Aids. We all get older. With age comes more wisdom, but also more situations..
Read more
Ergonomic Office Orthopaedic Chair: Your Ultimate..
Upgrade Your Workspace with our Ergonomic Office Orthopedic Chair. Introduction Back pain can be a formidable foe, especially for those of us who..
Read more
Exercise, fitness and Gym products
Exercise, fitness and Gym products! Attention fitness enthusiasts! Looking for a way to stay in shape and live a healthy, active lifestyle?..
Read more
Breast prosthesis
What is a Prosthetic external silicone Breast? A breast prosthesis, or a breast implant or form, is a synthetic breast-shaped device used to replace a..
Read more
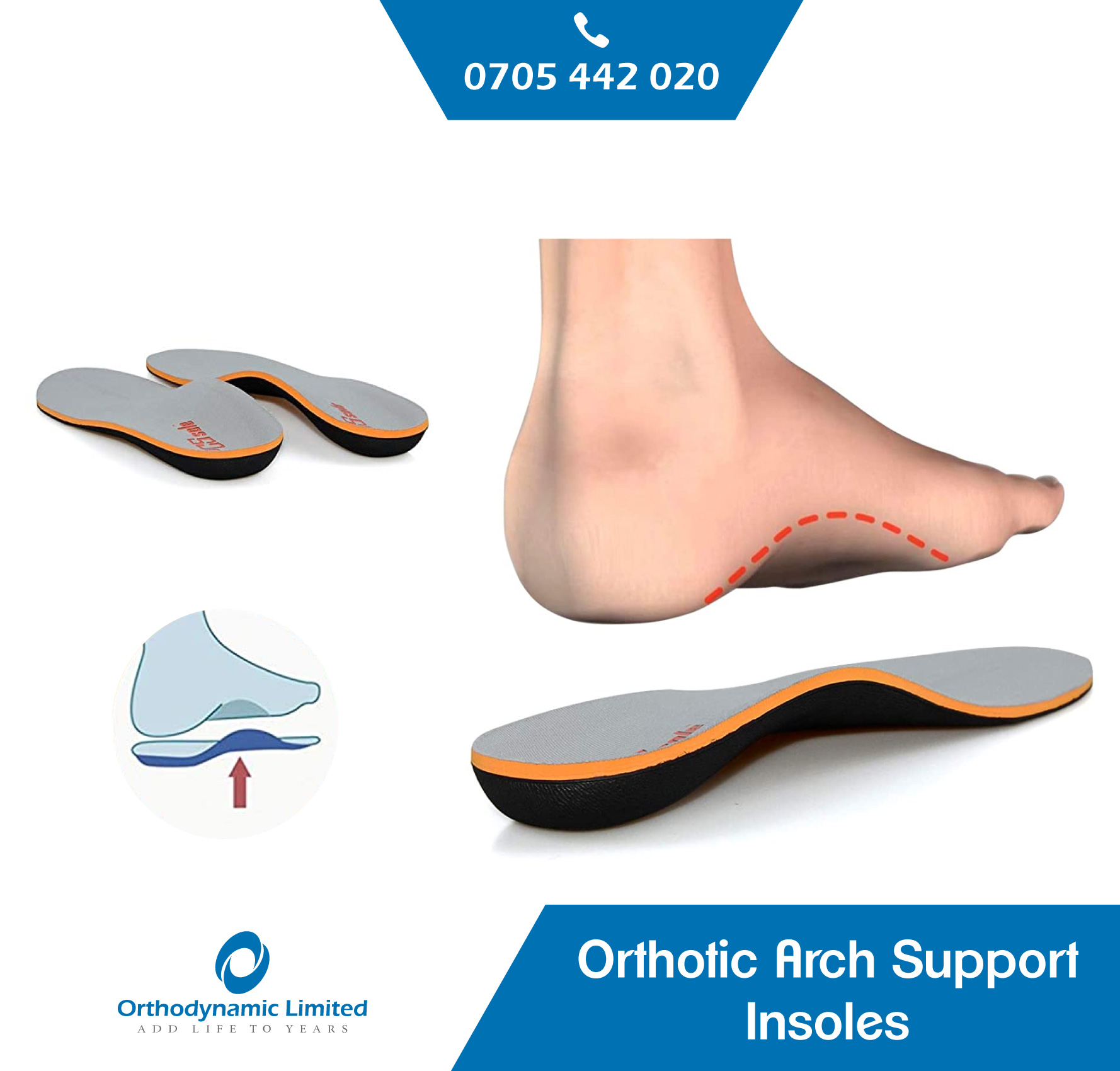
How do Plantar Fasciitis Arch Insole Sleeves for..
How do Plantar Fasciitis Arch Insole Sleeves for Pain work? Plantar fasciitis arch insole sleeves are designed to provide additional support to the..
Read more
How do reflexology massage slippers work?
How do reflexology massage slippers work? Reflexology massage slippers provide targeted stimulation to specific areas of the feet, which are believed..
Read more